Unveiling Iran's Majority: Demographics, Culture, And Growth
Iran, a land steeped in ancient history and vibrant culture, is also a nation of impressive demographic scale and diversity. With a population estimated at 92.4 million as of 2025, it stands as the 17th largest country in the world by population, a testament to its significant human capital and expansive landscape. Understanding the intricate tapestry of its people, particularly the majority population in Iran, is crucial for grasping the nation's identity, societal dynamics, and future trajectory.
This article delves into the demographic realities of Iran, exploring the composition of its majority population, their cultural influence, and the broader trends shaping the country's human landscape. We will examine the latest population figures, the concept of "Iranic peoples," and the undeniable dominance of the Persian ethnic group, alongside the significant role of urbanization and ongoing population growth.
Table of Contents
- Iran's Demographic Landscape: A Snapshot
- The Concept of "Iranic Peoples": Defining the Majority
- Persians: The Undisputed Majority Population in Iran
- Beyond Persians: Other Significant Iranic Groups
- Urbanization and Population Density: Shaping the Majority's Lifestyle
- Population Growth Trends and Future Projections
- Religious Landscape and Ethnic Minorities
Iran's Demographic Landscape: A Snapshot
To truly understand the majority population in Iran, it's essential to first grasp the overall demographic picture. As of the beginning of 2024, the population of Iran was estimated at 89.8 million. This figure reflects a consistent growth, with an average annual growth rate of 1.06% over the country’s population in 2023, according to United Nations data. Looking ahead, projections for 2025 place Iran's population at approximately 92.42 million, an increase from 91.57 million in 2024. More precisely, as of Friday, March 28, 2025, the current population of the Islamic Republic of Iran is recorded as 92,193,571, based on Worldometer’s elaboration of the latest United Nations data.
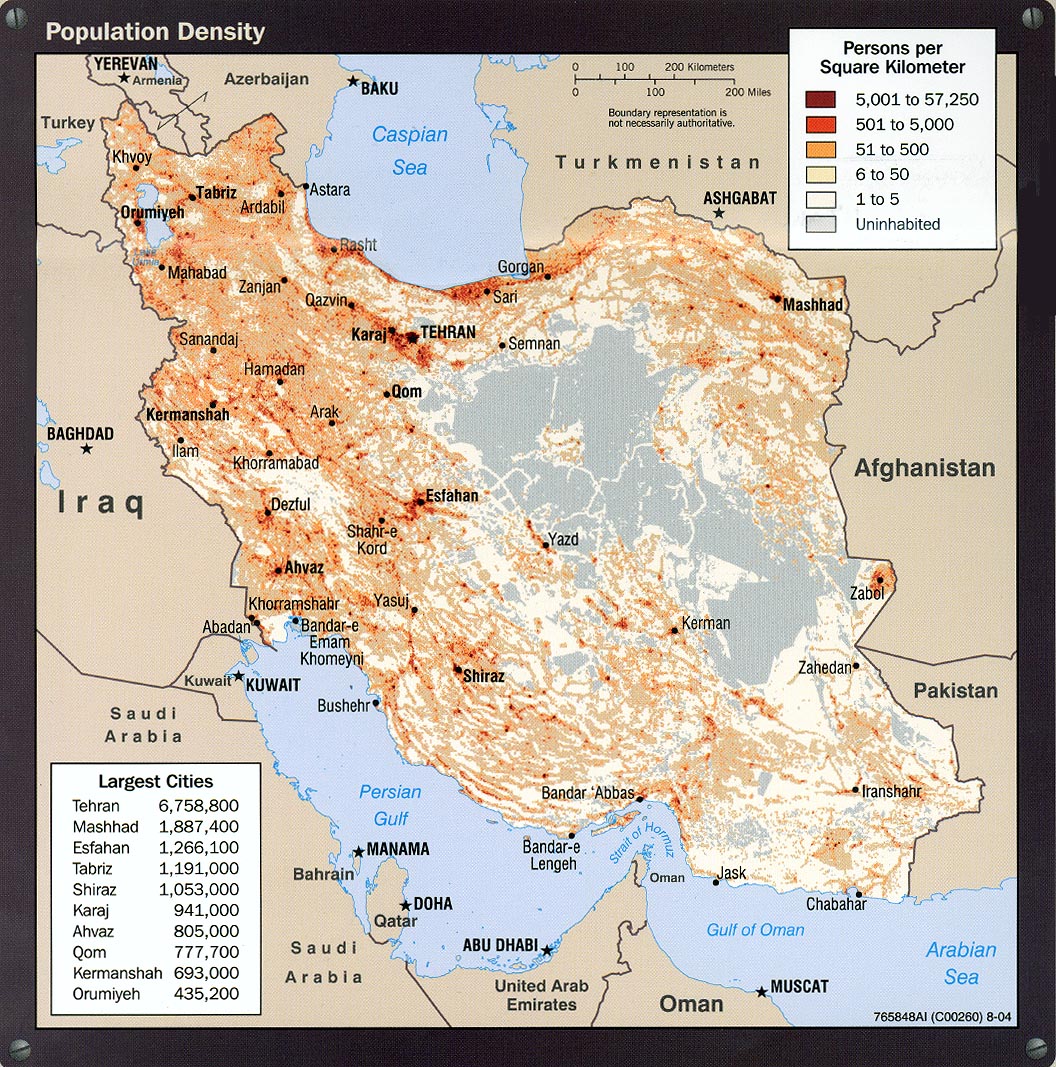
Iran's population growth has been remarkable over the decades. The 2016 population census reported 79.9 million people, marking a fourfold increase since 1956. Notably, between 1976 and 1986, the country experienced an average annual population growth of almost 4%, a period of rapid expansion that significantly shaped its current demographic profile. This robust growth has led to a population density of 57 people per km² (147 people per mi²) in 2025, calculated on a total land area of 1,628,550 km² (628,786 sq mi).
Urbanization is another defining feature of Iran's demographic landscape. Currently, a significant 73.3% of the population resides in urban areas, accounting for an estimated 67,760,281 people in 2025. This high level of urbanization concentrates a vast segment of the population, including the majority group, into cities, influencing everything from infrastructure development to cultural trends and economic activities. Understanding these foundational numbers provides the context for a deeper dive into who constitutes the majority population in Iran.
The Concept of "Iranic Peoples": Defining the Majority
When discussing the majority population in Iran, it's important to first introduce the broader ethno-linguistic category known as "Iranic peoples." This term encompasses a diverse group of ethnic communities who speak Iranian languages and share historical and cultural roots, originating from the ancient Iranian plateau. The data indicates that Iranic peoples collectively make up the overwhelming majority of Iran's inhabitants, comprising approximately 67% to 80% of the total population. Some sources even suggest this figure is closer to 80%, underscoring their numerical dominance.
This category is not monolithic but rather a mosaic of distinct groups, all of whom trace their heritage to the ancient Indo-Iranian migrations. Within this vast umbrella, several prominent groups exist, with varying sizes and geographical concentrations across the country. While the term "Iranic peoples" provides a broad classification, it is within this framework that we find the specific ethnic group that forms the absolute majority, influencing the nation's culture, politics, and social fabric more profoundly than any other. This foundational understanding helps to contextualize the subsequent discussion of the Persian people, who stand at the forefront of this demographic reality.
Persians: The Undisputed Majority Population in Iran
Within the larger family of Iranic peoples, the Persians (often referred to as Fars) constitute the undisputed and most significant majority population in Iran. Their numerical dominance is consistently highlighted across various demographic analyses. Estimates for the Persian share of the population vary slightly among different sources, but they consistently place Persians as the largest and majority ethnic group. Some data points suggest Persians make up more than half of the nation's population, while others indicate they constitute about 51% of Iran's dominant population. More specifically, figures often cite Persians as comprising approximately 61% of the population. Regardless of the precise percentage, the consensus is clear: Persians are the largest ethnic group in Iran and form its majority population.
This majority group is not evenly distributed across the vast Iranian landscape. Persians are primarily concentrated in the central, southern, and eastern regions of the country, forming dense populations in major cities and historical heartlands. Their historical presence and continuous cultural evolution have cemented their position as the demographic and cultural backbone of the nation. The sheer size of the Persian population means that their characteristics, traditions, and aspirations often define the broader national identity, making them a pivotal force in all aspects of Iranian life. Understanding the Persian majority is therefore fundamental to comprehending contemporary Iran.
Cultural Dominance and Influence
The numerical dominance of the Persian ethnic group has translated into a profound and pervasive cultural impact across Iran. Due to Persian dominance, the group’s culture has had a significant influence on other cultures in the country, shaping the national narrative, artistic expressions, and social norms. This influence is evident in several key areas. Firstly, the Persian language, Farsi, is the official language of Iran and serves as a lingua franca, unifying diverse ethnic groups across the nation. Its rich literary tradition, spanning centuries of poetry, philosophy, and prose, forms a cornerstone of Iranian identity and is widely studied and appreciated.
Beyond language, Persian cultural elements permeate Iranian society through art, architecture, music, cuisine, and traditional customs. The intricate designs of Persian carpets, the majestic architecture of ancient Persepolis and Islamic-era mosques, the soulful melodies of classical Persian music, and the elaborate celebrations of Nowruz (the Persian New Year) are all examples of this deep cultural imprint. These elements are not confined to Persian-speaking regions but are embraced and adapted by other ethnic groups, contributing to a shared national heritage. This cultural diffusion fosters a sense of collective identity, even as distinct regional and ethnic traditions continue to thrive. The enduring legacy of Persian culture underscores its central role in defining what it means to be Iranian.
Beyond Persians: Other Significant Iranic Groups
While Persians undeniably form the majority population in Iran, it is crucial to recognize that the category of "Iranic peoples" is broad and includes several other substantial ethnic groups. These groups, though smaller in number than the Persians, contribute significantly to Iran's rich cultural mosaic and hold distinct historical and linguistic identities. Among the largest of these other Iranic groups are the Kurds. The Kurds are a prominent ethnic community with a strong presence in the western and northwestern regions of Iran, particularly along the border with Iraq and Turkey. They possess their own distinct language (Kurdish, an Iranic language), vibrant cultural traditions, and a deep sense of historical identity.
In addition to Kurds, other notable Iranic communities include the Gilakis and Mazandaranis, who predominantly inhabit the Caspian Sea provinces of Gilan and Mazandaran, respectively. These groups speak their own specific Iranic languages, Gilaki and Mazandarani, and have unique regional customs, cuisines, and folk traditions shaped by their distinctive geographical environments. While not forming a majority themselves, their collective presence alongside the Persians underscores the diverse nature of Iranic populations within the country. Understanding these groups is essential for appreciating the full spectrum of Iran's ethno-linguistic heritage, which extends far beyond just the dominant Persian identity.
Iran's Ethnic Tapestry: A Diverse Nation
Looking beyond the Iranic peoples, Iran is truly an ethnically diverse country, a fact highlighted by the observation that its current population of over 80 million people is ethnically varied. This diversity extends beyond the Persian, Kurdish, Gilaki, and Mazandarani groups to include a range of non-Iranic communities, each contributing to the nation's vibrant cultural tapestry. While the provided data focuses on the majority, it is important to acknowledge the presence of other significant ethnic groups such as Azeris, who are a Turkic-speaking people primarily concentrated in the northwest; Arabs, found predominantly in the southwestern provinces; Baluchis, inhabiting the southeastern regions; and Turkmen, in the northeast, among others. Each of these groups maintains its unique language, customs, and traditions, enriching the overall cultural landscape of Iran.
This rich ethnic mosaic, while adding to the nation's cultural depth, also presents unique dynamics in terms of social cohesion and regional identity. The interplay between the dominant Persian culture and the distinct traditions of these minority groups is a constant feature of Iranian society. The presence of such diverse communities underscores that while the majority population in Iran is Persian, the country's identity is a complex blend of many different peoples, all coexisting within its borders. This intricate ethnic composition is a defining characteristic of Iran, reflecting centuries of migration, interaction, and cultural exchange.
Urbanization and Population Density: Shaping the Majority's Lifestyle
The demographic trends of urbanization and population density play a crucial role in shaping the daily lives and experiences of the majority population in Iran. As highlighted earlier, a significant 73.3% of Iran's population is urban, with an estimated 67,760,281 people residing in cities in 2025. This high rate of urbanization means that the vast majority of Persians, as the dominant ethnic group, live in urban centers, from the sprawling metropolis of Tehran to other large provincial cities. This concentration in urban environments has profound implications for their lifestyle, access to services, economic opportunities, and cultural practices.
Urban living often entails greater exposure to modern amenities, educational institutions, and diverse professional pathways. It also fosters a more interconnected and dynamic social environment, where traditional values may blend with contemporary influences. The high urban concentration also contributes to the overall population density of 57 people per km², which, while not extreme on a global scale, reflects the distribution of people across Iran's varied terrain, much of which is arid or mountainous. In urban areas, this density is, of course, far higher, leading to bustling cityscapes, complex transportation networks, and the constant evolution of urban infrastructure.
For the majority population, urbanization signifies a shift from agrarian or rural livelihoods to more industrialized or service-oriented economies. It influences family structures, leisure activities, and even political engagement. The challenges associated with rapid urbanization, such as housing, traffic, and environmental concerns, disproportionately affect the majority living in these densely populated areas. Conversely, the benefits of urban life, including better healthcare and educational opportunities, are also primarily experienced by this segment of the population. Thus, the urban fabric of Iran is inextricably linked to the demographic realities of its majority, defining much of their contemporary existence.
Population Growth Trends and Future Projections
Iran's population has been on a steady upward trajectory, a trend that continues to shape the demographic landscape for the majority population in Iran. The total population in Iran has grown consistently over recent decades and is expected to surpass 90 million in 2028. This growth is not merely a statistical figure but represents an ongoing expansion of the nation's human resources and potential. At the beginning of 2024, the population was estimated at 89.8 million, with an average annual growth rate of 1.06% compared to the population in 2023, according to data from the United Nations. This rate, while moderate, indicates a sustained increase in the number of Iranians, including the dominant Persian majority.
Looking further into the near future, projections confirm this upward trend. As of 2025, the population of Iran is projected at 92.42 million, a noticeable increase from 91.57 million in 2024. These projections highlight the demographic momentum that Iran possesses, driven by factors such as birth rates, mortality rates, and to a lesser extent, migration. For the majority population, this continued growth implies an expanding workforce, a larger consumer base, and potentially increased pressure on resources and infrastructure. It also means that the cultural and social characteristics of the majority will continue to be reinforced and expanded across the nation.
The historical context of this growth is also significant. The 2016 population census, which reported 79.9 million people, showcased a fourfold increase since 1956, demonstrating a long-term pattern of demographic expansion. The particularly high growth rate of almost 4% annually between 1976 and 1986 had a profound impact, creating a large youth bulge that is now maturing and continuing to contribute to population growth. Understanding these trends is vital for policymakers, urban planners, and social scientists alike, as they prepare for the evolving needs and characteristics of Iran's growing population, with the majority at its core.
Data Sources and Reliability
The accuracy and reliability of population data are paramount for any meaningful demographic analysis, especially when discussing the majority population in Iran. The figures and projections presented for Iran are based on information from several credible sources. For instance, population figures for Iran are often based on data from the Iran Open Data Portal, which provides estimated population figures for years like 2024. This governmental portal aims to offer transparent and accessible statistical information to the public and researchers.
Furthermore, the United Nations plays a crucial role in collecting and disseminating global demographic data. Many of the projections and growth rates, such as the 1.06% annual growth rate, are derived from United Nations data, which provides a standardized and internationally comparable framework for population statistics. Worldometer, a popular real-time statistics website, also elaborates on the latest United Nations data to provide current population estimates, such as the figure of 92,193,571 for March 28, 2025. These sources are considered authoritative in the field of demography.
Historical data also contributes to our understanding. For example, the 2016 population census, which reported Iran's population at 79.9 million, serves as a significant benchmark for understanding past growth trends. National censuses are fundamental for providing detailed snapshots of a country's population composition. The combination of national statistical agencies, international organizations, and reputable data aggregators ensures that the information on Iran's population, including its majority, is as accurate and reliable as possible, allowing for informed analysis and planning.
Religious Landscape and Ethnic Minorities
The religious landscape of Iran is deeply intertwined with its ethnic composition, offering another lens through which to understand the dynamics of the majority population in Iran. While the vast majority of Iranians are Muslims, there is a significant distinction between Shia and Sunni branches of Islam, and this division often correlates with ethnic lines. The dominant population, primarily Persians, are overwhelmingly adherents of Shia Islam, which is also the official state religion of Iran. This religious alignment further solidifies the cultural and social influence of the Persian majority, as their religious identity is closely tied to the national identity and state institutions.
In contrast, the data indicates that in Iran, most Sunni Muslims belong to ethnic minority groups. This observation is crucial for understanding the socio-religious fabric of the country. For example, many Kurds, Baluchis, and Turkmen, who are significant ethnic minorities, predominantly practice Sunni Islam. This creates a distinct religious and ethnic identity for these groups, setting them apart from the Shia Persian majority. While religious freedom is constitutionally protected for recognized minorities, the majority's religious affiliation inevitably shapes the country's cultural norms, legal framework, and public discourse.
The Interplay of Ethnicity and Religion
The interplay between ethnicity and religion in Iran is a complex yet fundamental aspect of its societal structure. For the majority population, being Persian often goes hand-in-hand with being a Shia Muslim, creating a powerful sense of shared identity and cultural cohesion. This strong alignment has historically contributed to the stability of the state and the perpetuation of national traditions. The cultural dominance of the Persian group, as discussed earlier, is therefore amplified by its religious majority status, influencing everything from educational curricula to public holidays and social customs.
Conversely, for ethnic minorities who are predominantly Sunni, their religious identity can reinforce their distinct ethnic identity, sometimes leading to unique challenges and considerations within a Shia-majority state. While Iran officially recognizes the rights of religious minorities, the socio-political landscape is undeniably shaped by the majority's religious orientation. This dynamic highlights the multifaceted nature of identity in Iran, where ethnicity, language, and religion often converge to define group affiliations and shape individual experiences. Understanding this interplay is essential for a comprehensive grasp of the diverse and intricate human tapestry that constitutes Iran.
Conclusion
Iran is a nation of profound demographic depth and diversity, yet at its core lies a clear majority population: the Persians. With a current population of over 92 million and steady growth, Iran stands as a significant global player in terms of human capital. The Iranic peoples, comprising 67% to 80% of the total, form the broader ethno-linguistic base, with Persians consistently making up the largest share, ranging from 51% to 61% of the population, and predominantly concentrated in the central, southern, and eastern regions. This demographic dominance has allowed Persian culture to profoundly influence the entire nation, shaping its language, arts, and societal norms.
Beyond the majority, Iran's rich ethnic tapestry includes other significant Iranic groups like the Kurds, Gilakis, and Mazandaranis, as well as various non-Iranic minorities, contributing to a vibrant and complex cultural landscape. The country's high urbanization rate, with nearly three-quarters of its population living in cities, further defines the lifestyle and opportunities for the majority, while ongoing population growth trends suggest a continued expansion of Iran's human resources into the future. The close link between the Persian majority and Shia Islam also underscores the intricate interplay of ethnicity and religion in shaping national identity. Understanding these demographic realities is not just about numbers; it's about appreciating the dynamic forces that shape one of the world's most historically rich and culturally significant nations.
What are your thoughts on Iran's demographic evolution? Share your insights in the comments below, and don't forget to share this article with anyone interested in understanding the fascinating human landscape of Iran. Explore more of our articles to deepen your knowledge of global demographics and cultural trends!
Iran Population Density Map - Iran • mappery

Population of Iran - Chronicle Fanack.com

Population of Iran - Chronicle Fanack.com