Iran's Population 2025: Unpacking Demographic Estimates
Understanding the future trajectory of a nation's population is a complex yet crucial endeavor, offering invaluable insights into its socio-economic fabric, resource demands, and potential challenges. As we look towards the middle of the decade, the "current population of Iran 2025 estimate" becomes a focal point for demographers, policymakers, and international observers alike. This estimate isn't merely a number; it represents the culmination of intricate demographic trends, policy impacts, and unforeseen global influences, painting a vital picture of Iran's evolving human landscape.
Much like upgrading to a new model of technology, understanding demographic shifts requires a careful assessment of the "current" situation while anticipating future needs and capabilities. Just as one might analyze the performance of a "current phone" or the features of a "current plan" before making a decision, projecting a nation's population for 2025 demands a thorough examination of its present demographic structure and the forces shaping its growth or decline. This article delves into the methodologies, factors, and implications surrounding Iran's projected population for 2025, aiming to provide a comprehensive and accessible overview for a general audience.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Iran's Demographic Landscape
- Key Factors Shaping Iran's Population
- Mortality and Life Expectancy in Iran
- The Role of Migration in Population Dynamics
- Economic and Social Influences on Demographics
- Projecting Iran's Population for 2025
- Challenges and Opportunities Arising from Population Shifts
- The Future Outlook: What Lies Beyond 2025?
Understanding Iran's Demographic Landscape
Iran, a nation with a rich history and diverse geography, has experienced significant demographic transformations over the past few decades. From rapid population growth in the late 20th century to a dramatic decline in fertility rates, its demographic journey has been unique and multifaceted. Understanding the "current" state of its population is the essential first step before any meaningful "estimate" for 2025 can be made. This involves looking at the size, age structure, and distribution of its people. Just as one might assess their "current uverse s20 receiver" to understand its capabilities before programming a new remote, demographers meticulously analyze existing data from censuses, vital statistics registries, and surveys. This foundational data allows them to grasp the nuances of Iran's demographic reality, including the proportion of young people, working-age adults, and the elderly, which are critical indicators for future trends.Historical Context and Recent Trends
In the post-revolutionary period of the 1980s, Iran witnessed a pronounced baby boom, driven by pro-natalist policies and socio-cultural factors. This led to a very young population structure. However, by the early 1990s, the government shifted its stance, implementing one of the most effective family planning programs in the world. This swift policy change, coupled with increased female education and urbanization, led to a remarkably rapid decline in fertility rates, moving from over six children per woman to below replacement level in just a few decades. This demographic transition has profound implications. The large cohorts born in the 1980s are now entering their prime working and reproductive ages, creating a "youth bulge" that presents both opportunities and challenges. As these cohorts age, Iran will experience a significant shift towards an older population structure, a phenomenon common in many developed nations but occurring at an accelerated pace in Iran. This rapid shift means that the demographic "current" is strong and will continue to shape the "current population of Iran 2025 estimate."Key Factors Shaping Iran's Population
Several interconnected factors play a pivotal role in determining a nation's population size and structure. For Iran, these include fertility rates, mortality rates, and migration patterns. Each of these elements acts as a variable in the complex equation that yields a population estimate for 2025. Much like troubleshooting a phone that "has an issue with intermittently resetting itself," understanding the root causes of demographic shifts requires a deep dive into these fundamental components.Fertility Rates and Family Planning Policies
Iran's fertility rate has been a subject of considerable policy attention and public debate. After achieving remarkable success in reducing birth rates in the 1990s and early 2000s, the government has, in recent years, reversed course, actively promoting larger families to counter concerns about an aging population and potential future labor shortages. Policies include incentives for childbirth, restrictions on family planning services, and cultural campaigns encouraging marriage and reproduction. The effectiveness of these pro-natalist policies is a key determinant for the "current population of Iran 2025 estimate." While some sources suggest a slight uptick in birth rates in response to these measures, the long-term trend of declining fertility due to urbanization, education, and economic pressures remains a powerful force. The impact of these policies by 2025 will depend on their sustained implementation and the degree to which they can counteract deeply ingrained societal trends. It's a bit like trying to "program the new s20 remote" to control a system that has its own established patterns; the outcome isn't always immediate or perfectly predictable.Mortality and Life Expectancy in Iran
Another critical component of population dynamics is mortality. Improvements in healthcare, sanitation, and living standards generally lead to lower death rates and increased life expectancy. Iran has made significant strides in this area, with life expectancy at birth steadily increasing over the past few decades. This means people are living longer, contributing to a larger overall population and an aging demographic structure. However, challenges remain. Non-communicable diseases, environmental factors, and access to advanced medical care in all regions can influence mortality rates. For the "current population of Iran 2025 estimate," a stable or improving mortality rate suggests continued population growth, particularly among older age groups. Conversely, any significant health crises or setbacks could have an impact, though typically less dramatic than shifts in fertility or migration in the short term. The reliability of "current" health data is paramount, just as knowing if your "current phone" is holding a charge is crucial before embarking on a long journey.The Role of Migration in Population Dynamics
Migration, both internal and international, plays a significant, albeit often less predictable, role in shaping a nation's population. For Iran, this includes the movement of people within its borders (urbanization, regional shifts) and the flow of people across its international boundaries (emigration and immigration).Internal and International Movements
Internal migration in Iran has largely been characterized by a movement from rural areas to urban centers, particularly Tehran and other major cities. This trend contributes to urbanization and can strain urban infrastructure while depopulating rural areas. These internal shifts don't change the national total but significantly alter population distribution and resource demands. International migration is more complex. Iran has historically been a host to a large refugee population, primarily from Afghanistan, and has also experienced emigration of its own citizens, often driven by economic opportunities, political considerations, or social factors. The net effect of these movements – whether more people are entering or leaving the country – directly impacts the "current population of Iran 2025 estimate." For instance, "considerably current labor shortages all industries are facing" in some sectors globally could influence outward migration, while regional conflicts might lead to inward migration. This "unknown factor" makes precise forecasting challenging, much like predicting if changing your "current plan" will result in losing a "bogo credit" – there are always specific qualifications and unforeseen consequences.Economic and Social Influences on Demographics
Beyond the direct demographic variables, broader economic and social conditions exert a profound influence on population trends. These include economic stability, employment opportunities, education levels, women's empowerment, housing costs, and cultural norms. Economic conditions, for instance, can significantly impact fertility rates. In times of economic hardship or uncertainty, families may choose to have fewer children. Conversely, improved economic prospects might encourage larger families. The availability of jobs, particularly for the youth bulge, is critical. If there are "missing credits" in job creation or if "overdue bills" (economic pressures) accumulate, it can lead to social unrest or increased emigration, directly affecting the "current population of Iran 2025 estimate." Social factors, such as the increasing participation of women in higher education and the workforce, tend to correlate with lower fertility rates. Urbanization also plays a role, as city dwellers often have different family planning behaviors compared to rural populations. Cultural norms and religious beliefs, while evolving, also continue to shape family size preferences. Understanding these intricate interplays is essential for accurate demographic projections. It's not just about getting a "new model" phone; it's about how that new model fits into your entire "current" lifestyle and budget.Projecting Iran's Population for 2025
Estimating a nation's population for a future year like 2025 involves sophisticated demographic models that take into account the factors discussed above. These models typically use the "current" population as a baseline and then apply assumptions about future fertility, mortality, and migration rates.Methodologies and Potential Scenarios
The most common method for population projection is the cohort-component method. This approach tracks different age and sex cohorts over time, applying age-specific fertility rates to the female cohorts, age-specific mortality rates to all cohorts, and net migration figures. Reputable international organizations like the United Nations, the World Bank, and national statistical agencies (like the Statistical Centre of Iran) regularly produce such projections. However, projections are not predictions; they are conditional on the assumptions made. Different scenarios can be modeled: a "high" variant assuming higher fertility or net immigration, a "medium" variant based on current trends, and a "low" variant assuming lower fertility or net emigration. For the "current population of Iran 2025 estimate," the medium variant is often considered the most likely, but it's crucial to acknowledge the range of possibilities. Just as you might "consider having (2) ISPs if working from home, as nothing" is foolproof, demographers often use multiple models and data sources to increase the robustness of their estimates. Relying on a single data point, even if it's a "Samsung Galaxy 9 Plus" of data, isn't enough for a comprehensive picture. Based on various sources, the "current population of Iran 2025 estimate" generally hovers around **89-90 million people**. For instance, the United Nations' World Population Prospects 2022 revision projects Iran's population to be approximately 89.4 million in 2025 under its medium variant. Other national and international bodies might offer slightly different figures based on their specific assumptions and data adjustments, but the overall trend points towards continued, albeit slowing, growth. This growth is primarily driven by the momentum from past high birth rates, even as current fertility remains low.Challenges and Opportunities Arising from Population Shifts
The "current population of Iran 2025 estimate" and its underlying trends present both significant challenges and unique opportunities for the nation. **Challenges:** * **Aging Population:** As the large youth bulge ages, Iran will face increasing demands on its healthcare system, pension schemes, and social services. This demographic shift requires proactive planning to avoid a situation where the system "intermittently resets itself" or faces "overdue bills" in terms of social welfare. * **Labor Market Dynamics:** While the youth bulge initially provides a demographic dividend (a large working-age population), if sufficient jobs are not created, it can lead to high unemployment and social frustration. The "considerably current labor shortages all industries are facing" globally might suggest opportunities for Iranian labor, but domestic job creation remains paramount. * **Resource Management:** A growing population, even if slowing, places continued pressure on natural resources like water, energy, and food, especially in a country already facing environmental challenges. * **Regional Disparities:** Internal migration patterns can exacerbate disparities between urban and rural areas, leading to issues of unequal access to services and opportunities. **Opportunities:** * **Demographic Dividend (for a limited time):** The large working-age population can still be a powerful engine for economic growth if effectively utilized through investment in education, skills training, and job creation. * **Innovation and Entrepreneurship:** A young and educated population can be a source of innovation and entrepreneurship, driving economic diversification. * **Human Capital Development:** Continued investment in education and health can enhance the quality of human capital, leading to a more productive workforce. Addressing these challenges and seizing these opportunities requires robust policy planning, much like ensuring you "pay every bill on time without fail" to avoid future problems. It's about adapting to the "new model" of demographic reality.The Future Outlook: What Lies Beyond 2025?
While our focus has been on the "current population of Iran 2025 estimate," it's crucial to consider the longer-term trajectory. Beyond 2025, Iran is projected to continue its demographic transition towards an older population structure. The pace and extent of this aging will depend heavily on the success of current pro-natalist policies and the future trends in migration. The experiences of other nations that have undergone similar demographic shifts offer valuable lessons. Countries like Japan and many in Europe are grappling with the socio-economic implications of rapidly aging populations and declining birth rates. Iran can learn from these experiences, proactively developing strategies to manage its demographic future. This includes fostering a dynamic economy capable of supporting an older population, ensuring social security and healthcare systems are robust, and potentially exploring policies to attract skilled immigration. Just as one might assess if they can "move the sim card from your current phone to the new phone" or if a "replacement" is needed due to a "different size," nations must adapt their policies to changing demographic realities. The "current population of Iran 2025 estimate" is not just a static number; it's a snapshot in a dynamic process, a crucial data point in understanding Iran's journey towards its demographic destiny. The ability to effectively harness this demographic dividend and mitigate the challenges of an aging society will be key to Iran's sustainable development in the decades to come.Conclusion
The "current population of Iran 2025 estimate" stands as a testament to the profound demographic shifts Iran has experienced. Projecting around 89-90 million people, this figure reflects a nation in transition, grappling with the legacy of past high fertility, the rapid decline that followed, and recent efforts to reverse course. Key factors like fertility rates, mortality improvements, and migration patterns are the bedrock of these estimates, each influenced by complex economic, social, and policy environments. Understanding these dynamics is vital for effective governance and resource allocation. While the "Data Kalimat" provided for this analysis, such as concerns about "intermittently resetting itself" or "overheating and not holding a battery charge" in a device, might seem far removed from population statistics, they offer a powerful analogy: just as technology requires constant monitoring, adaptation, and reliable data to function optimally, so too does a nation's demographic health. Ignoring "missing credits" in data or failing to address "overdue bills" in social policy can lead to unforeseen challenges. As Iran moves beyond 2025, its demographic landscape will continue to evolve, presenting both opportunities for growth through its large working-age population and challenges related to an aging society. The insights gained from these population estimates are invaluable for strategic planning, ensuring a resilient and prosperous future for all Iranians. We hope this comprehensive overview has shed light on the intricacies of Iran's population dynamics. What are your thoughts on the future demographic trends in Iran? Share your insights in the comments below, and consider sharing this article with others interested in global population studies. For more in-depth analyses of demographic shifts and their global implications, explore other articles on our site!
Electric Current - Definition, Types, Properties, Effects, FAQs
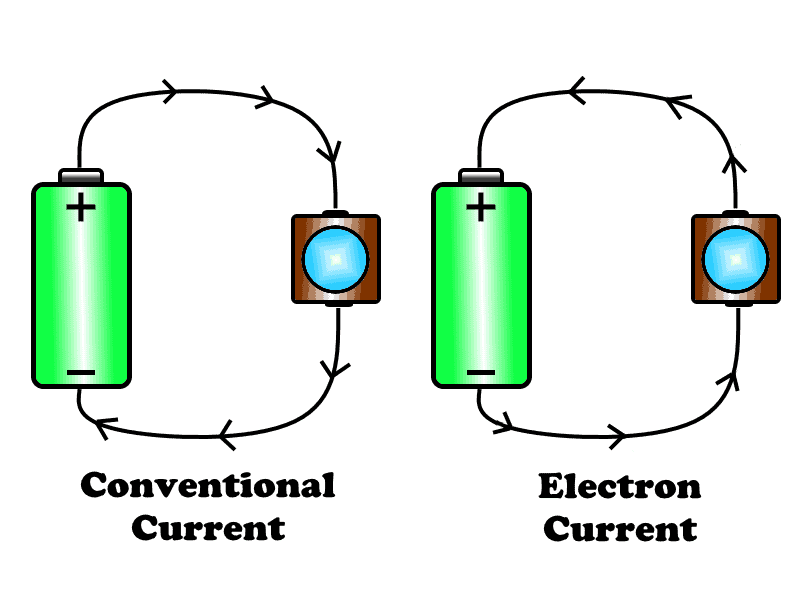
What is Electric Current? Unit, Formula, Types & Applications

What Is Electric Current? - Iken Edu - YouTube